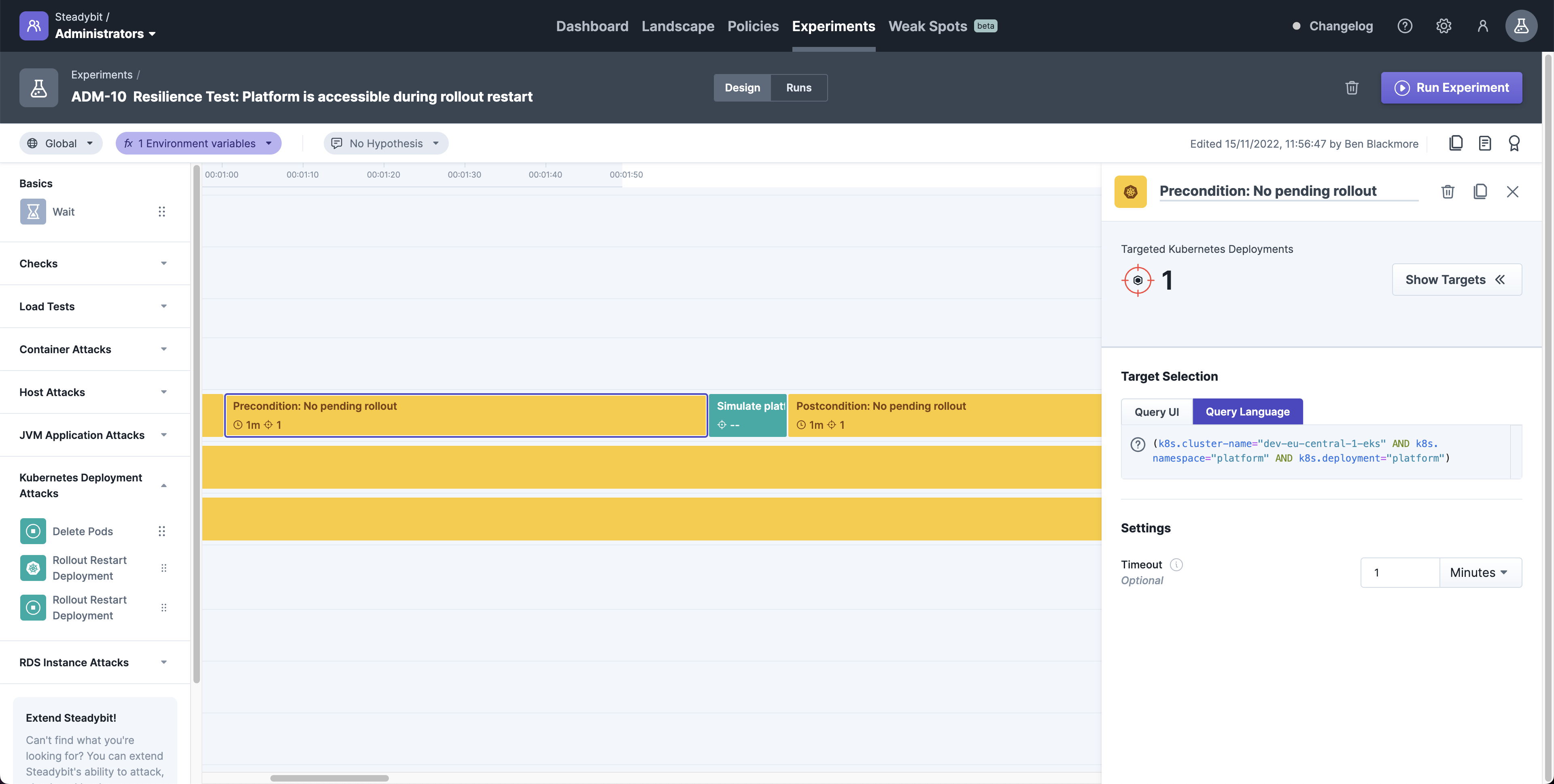
Deployment Rollout Status
Check the rollout status of the deployment. The check succeeds when no rollout is pending, i.e., kubectl rollout status exits with status code 0.
Targets:
Kubernetes Deployments
Deployment Rollout Status
Check the rollout status of the deployment. The check succeeds when no rollout is pending, i.e., kubectl rollout status exits with status code 0.Targets:
Kubernetes Deployments
Install nowDeployment Rollout Status
Check the rollout status of the deployment. The check succeeds when no rollout is pending, i.e., kubectl rollout status exits with status code 0.
Targets:
Kubernetes Deployments
Deployment Rollout Status
Check the rollout status of the deployment. The check succeeds when no rollout is pending, i.e., kubectl rollout status exits with status code 0.Targets:
Kubernetes Deployments
Install now