RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ
A Steadybit extension with various actions and check about RabbitMQ.RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ
A Steadybit extension with various actions and check about RabbitMQ.Introduction to the RabbitMQ Extension
The Steadybit RabbitMQ Extension allows you to inject chaos into RabbitMQ clusters and observe how your system behaves under stress conditions affecting queues, exchanges, nodes, and message flow.
Integration and Functionality
Integration of RabbitMQ into Steadybit works via the official RabbitMQ Management Plugin and its HTTP API, using the rabbithole Go client library.
The extension-rabbitmq leverages these APIs and AMQP connections to:
- Discover clusters, nodes, vhosts and queues
- Inspect queue metrics such as message backlog
- Manage policies dynamically to inject constraints or change behaviors
- Connect over AMQP(S) to simulate message publisher and check message flow
Some actions and checks require management access and, optionally, AMQP credentials for interacting with queues.
Integration of RabbitMQ in Steadybit
Discovery
The RabbitMQ Extension automatically discovers:
- Clusters and nodes (via management endpoints)
- Vhosts
- Queues, along with attributes like durability, auto-delete flags, bindings, and max length settings
Each discovered resource becomes a Steadybit target, allowing you to apply attacks or checks.
The extension supports dynamic chaos actions, including:
-
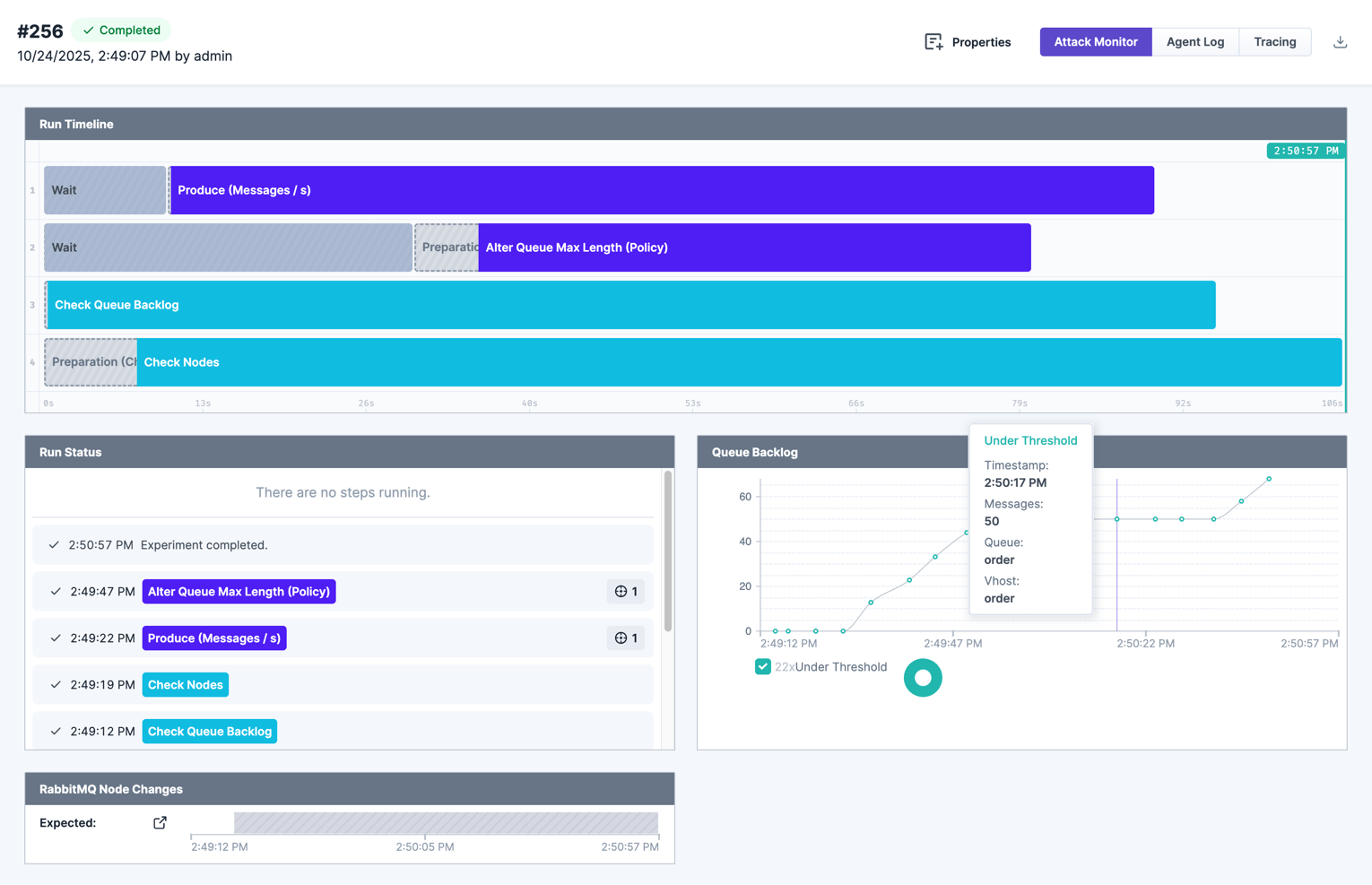
Alter Queue Max Length (Policy) Dynamically enforces a
max-lengthlimit on a queue using a temporary RabbitMQ policy. Useful to simulate queue overflow and message drops under constrained storage. -
Publish Messages Sends messages to one or more queues at a fixed rate or in fixed quantity to simulate load and measure consumer throughput.
Checks
Monitor RabbitMQ system health or message flow:
- Queue Backlog Check — Verify message number
- Cluster Node Check — Detect node unavailability or node alarms.
Installation and Setup
To integrate the RabbitMQ extension with your environment, follow our setup guide.